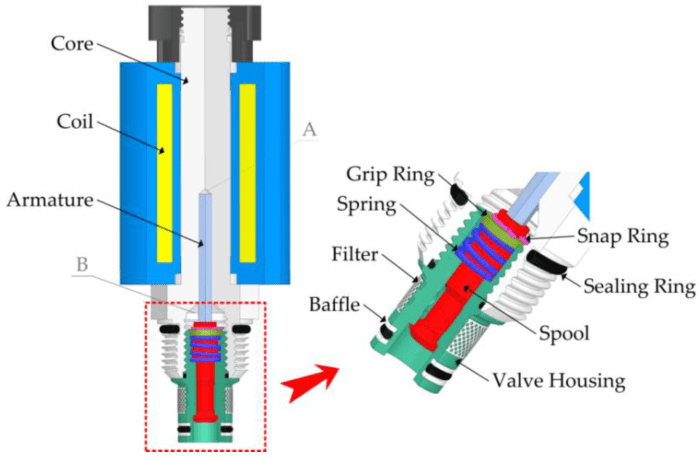
Up to what speed are snap in valves suitable for – Snap-in valves are a type of quick-connect valve that offers numerous advantages in various industrial applications. However, understanding the speed limitations of these valves is crucial to ensure optimal performance and system reliability. This article explores the factors influencing the speed suitability of snap-in valves, providing a comprehensive guide for engineers and technicians working with fluid systems.
This article delves into the relationship between flow rate, pressure, fluid compatibility, environmental factors, valve design, and installation practices to determine the maximum speed at which snap-in valves can operate effectively.
Flow Rate Considerations

The flow rate of a fluid through a snap-in valve is a critical factor in determining its suitability for a particular application. The following table provides a general guideline for the flow rates and corresponding suitable snap-in valve speeds:
| Flow Rate (GPM) | Suitable Snap-In Valve Speed (CPM) |
|---|---|
| 0-10 | Up to 120 |
| 10-25 | Up to 90 |
| 25-50 | Up to 60 |
| 50-100 | Up to 30 |
Factors that affect the flow rate through a snap-in valve include:
- Valve size
- Pressure
- Fluid properties (e.g., viscosity, density)
FAQ Compilation: Up To What Speed Are Snap In Valves Suitable For
What is the maximum flow rate for snap-in valves?
The maximum flow rate for snap-in valves varies depending on the valve size and design. Generally, smaller valves have lower flow rates, while larger valves can handle higher flow rates.
How does pressure affect the speed suitability of snap-in valves?
Pressure can affect the speed suitability of snap-in valves by influencing the valve’s ability to maintain a seal. Higher pressure can cause the valve to leak, which can reduce its flow rate and overall performance.
What types of fluids are compatible with snap-in valves?
Snap-in valves are compatible with a wide range of fluids, including water, oil, air, and gas. However, certain fluids, such as corrosive or abrasive fluids, may require special valve materials or coatings to ensure compatibility.