The fourth state of matter by jo ann beard – Embark on an illuminating journey into the enigmatic realm of plasma, the fourth state of matter. Discover its extraordinary properties, diverse applications, and the captivating frontiers of plasma science and technology, as we unravel the mysteries that lie within this ionized gas.
Plasma, the enigmatic fourth state of matter, captivates with its unique characteristics and myriad applications. Join us as we delve into its fascinating properties, explore its industrial and scientific significance, and uncover the exciting advancements shaping its future.
Plasma: An Overview

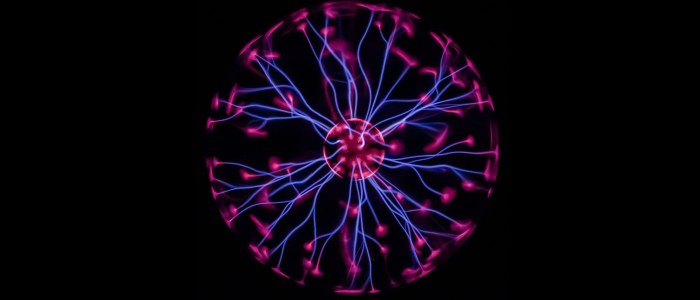
Plasma, the fourth state of matter, is a fascinating and complex substance that exhibits unique properties and behavior. Unlike solids, liquids, and gases, plasma is a highly ionized gas where a significant number of atoms have lost their electrons, resulting in a collection of positively charged ions and negatively charged free electrons.
Plasma is found abundantly throughout the universe, constituting over 99% of visible matter. It is present in stars, the solar wind, and the Earth’s ionosphere. Plasma also plays a crucial role in various scientific and industrial applications, such as plasma display panels, semiconductor fabrication, and plasma medicine.
Properties of Plasma, The fourth state of matter by jo ann beard
Plasma possesses distinct properties that set it apart from other states of matter. These properties include:
- Electrical Conductivity:Plasma is an excellent conductor of electricity due to the presence of free electrons. This property makes plasma useful in various electrical applications, such as plasma torches and ion propulsion systems.
- High Temperature:Plasma exists at extremely high temperatures, typically ranging from thousands to millions of degrees Celsius. The high temperature of plasma is attributed to the kinetic energy of the free electrons and ions.
- Low Density:Plasma has a low density compared to solids and liquids. This is because the free electrons and ions are spread out over a large volume, resulting in a relatively low particle density.
FAQ: The Fourth State Of Matter By Jo Ann Beard
What is the fourth state of matter?
Plasma is the fourth state of matter, characterized by its ionized gas, high temperature, and low density.
What are the unique properties of plasma?
Plasma exhibits high electrical conductivity, low viscosity, and the ability to generate magnetic fields.
Where is plasma found?
Plasma is prevalent in stars, lightning, and fluorescent lights, among other natural and man-made sources.